I. Overview of Master Data Management (MDM)
With enterprise IT landscapes growing increasingly complex, businesses that once relied on legacy data management systems or unsuited applications struggle to keep up with the growing data volume and variety as well as the speed of technological change.
Master Data Management (MDM) aims to address some of these critical data challenges arising from inaccurate, inconsistent, and unreliable data by streamlining the way data is managed in alignment with key business priorities.
MDM is a set of practices that brings together people, processes, and technologies existing within an enterprise ecosystem to improve information quality, value, and aid organizational performance.
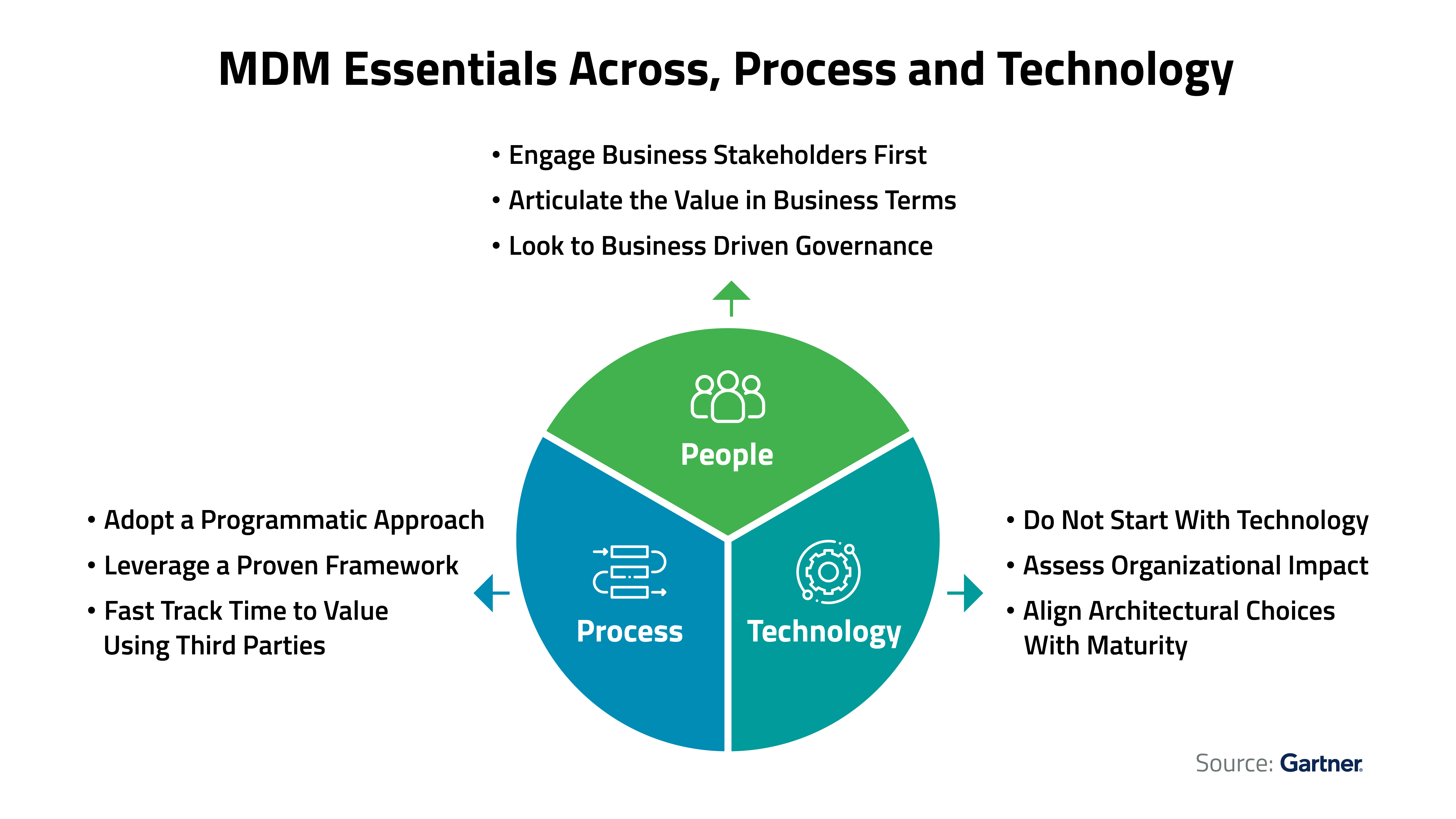
i. Defining MDM
MDM is a technology-driven business discipline that includes a set of strategies built on seamless collaboration between IT and business functions. It is intended towards ensuring uniformity, accuracy, governance, semantic consistency, and accountability of an organization’s core master data assets. Master data management involves seamless data acquisition, standardization, and integration of organizational data by maintaining a single, authoritative source of truth, also known as the “golden record.”
As a fundamental data management and governance practice to optimize data exchange between systems, master data management aids processes across diverse IT platforms, and enhances data reliability for business intelligence and decision-making.
ii) Difference between Single-domain and Multi-domain MDM?
Single-domain Master Data Management (MDM) focuses on a single data type, such as customer, product, or supplier information, ensuring data accuracy and uniformity only in a single domain. In contrast, multi-domain MDM ensures the accuracy and uniformity of multiple data domains under a cohesive governance structure, allowing organizations to interconnect related data across various business areas.
By offering a centralized and holistic perspective, a multi-domain MDM manages intricate data relationships to optimize decision-making, boost operational efficiency, and enhance data integrity across the enterprise.
II. Importance of MDM for Modern-day Businesses
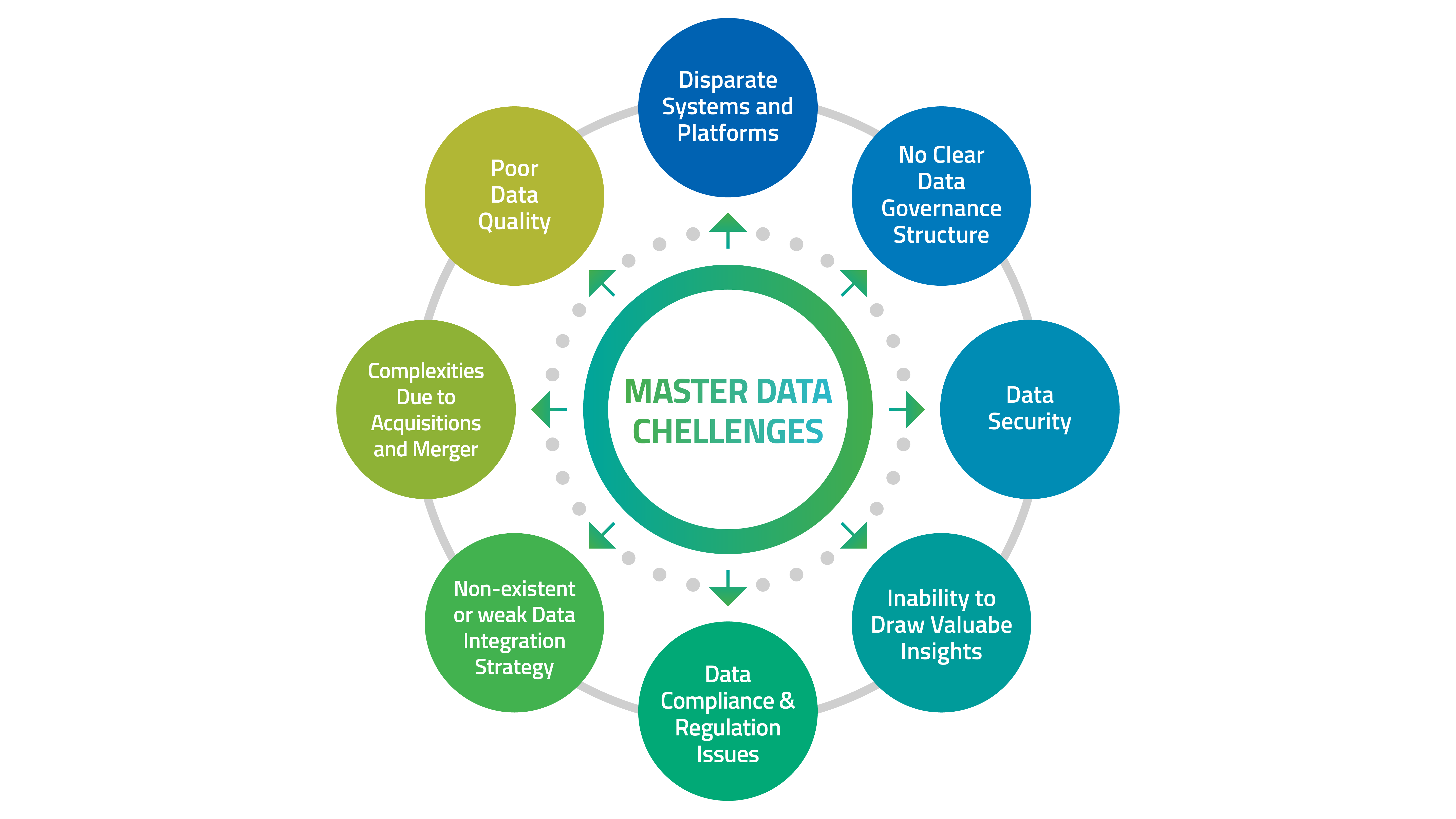
Modern-day organizations are grappling with the sheer scale of data generated across multiple systems and geographic locations, which is leading to isolated business processes, limited data visibility, and significant operational challenges.
It starts with fragmented data across complex IT landscapes, which hinders data trust and analysis. In addition, scalability issues, lack of integration across systems and complications arising from acquisitions and mergers pose significant challenges. Also, poor data quality demands considerable manual intervention which slows down analytics and AI adoption.
Besides, many organizations still view MDM as an IT initiative rather than a strategic one and are unable to understand its value.
On the other hand, the emergence of Industry 4.0, characterized by a mix of AI-fuelled analytics, Machine Learning (ML), Automation, and GenAI, has further intensified the challenges businesses face. To withstand these persistent pressures, managing and leveraging data effectively has become much more strategically important than before. And since master data is the most critical asset a company possesses, managing it optimally is now non-negotiable. MDM is essential to get a holistic and reliable view of master data, streamline business processes, and build business agility and resilience.
Also read: The Relevance of PIM in Driving Digital Transformation
III. What is Master Data?
i. Defining Master Data
Master data refers to the basic, non-transactional data around which an organization’s business is carried out. It comprises of established core data identifiers with regards to customers, suppliers, products, locations, and other elements. Even though master data is typically non-transactional in nature, it does include information that describes transactions. All master data is shared across several systems and departments and belongs to precise entities that aids a business to function and grow.
ii. Types of Master Data
Master data is typically divided into four primary categories.
- Products: Data attributes related to any product or service offered. Includes, product names, descriptions, technical specifications, pricing, SKUs, asset, equipment, bill of materials, etc.
Used in: Inventory management, marketing and sales platforms, eCommerce websites.
- Customers: Pertains to any individuals or businesses involved in purchasing goods and services. Includes, customer names, contact details, addresses, demographic data and preferences, and ordering history. Customer data also encompasses suppliers, partners, and employee information.
Used in: CRM systems, order management systems (OMS), customer service departments, marketing and sales departments.
- Locations: Includes physical sites and places where organizations perform their work. It consists of details of headquarters, facilities, agencies, stores, warehouses, branches, and franchises.
Used in: Regional sales strategies, logistical operations, distributions, shipments.
- Other: Refers to other business critical data such as business schedules, licenses, policies, contracts, certifications, vendor/supplier data, warranty details, and organizational structures.
Used in: Procurement, supply chain, accounts payable, relationship management, sales outreach, accounting, budgeting, and support interactions.
IV. Benefits of Master Data Management
With a shared single, trusted view of data, MDM serves as a foundation for business performance and supports long-term vision and strategy. Here are the main benefits of master data management platform:
- Data Accuracy and Consistency: By establishing a unique, authentic repository of data, MDM gets rid of redundancies and duplicates. It standardizes data formats and imposes data quality rules for maximum precision and consistency. This builds the foundation for reliable data-driven strategies and strong business processes.
- Agility and Scalability: Master data management helps organizations stay agile in responding to evolving technological and business shifts. It enables enterprises to scale operations smoothly, when it comes to expanding into newer markets, building additional business units or during mergers and acquisition for uninterrupted business growth.
- Operational Efficiency: By eliminating data silos MDM platform streamlines data management and create uncomplicated, faster, and efficient processes. This leads to increased efficiency, better data visibility, and quick access to correct information, allowing improved workflows and inter-departmental collaboration.
- Integration: MDM software integrates with various third-party systems and applications, such as CRMs, ERPs, etc., for continuous data exchange. It also ensures smoother new technology adoption, minimal disruption, and enterprise-wide data coherence, which lays the groundwork for innovation.
- Data Governance and Compliance: MDM helps businesses put robust governance framework in place by preparing policies regarding data access and protocols for clear accountability. Master data management solutions also enforces compliance for several industry-specific regulations (e.g., ACES/PIES), thereby reducing the risk of penalties and strengthening reputation.
- Decision-Making: With a unified and holistic view of data, organizations get the clarity they need to identify gaps, analyse patterns, spot trends, and uncover critical new insights. This enables teams to assess risks, make informed decisions, forecast better, explore fresh opportunities, and respond swiftly to market changes.
- Digital Transformation: MDM empowers businesses to harness the full potential of their data by building robust business processes and new capabilities, while seamless adopting emerging technologies such as advanced analytics, AI, ML, etc. This prepares them for current and future success while consolidating their market position.
- Customer Experience: By bringing together data from various sources, MDM offers a 360-degree view of customer and product master data domains. This allows businesses to target buyers with personalized campaigns according to their preferences, at the same time paving the way for long-term customer relationships and loyalty.
Also read: A Comprehensive Guide to Product Information Management (PIM) and Why It Is Trending Today?
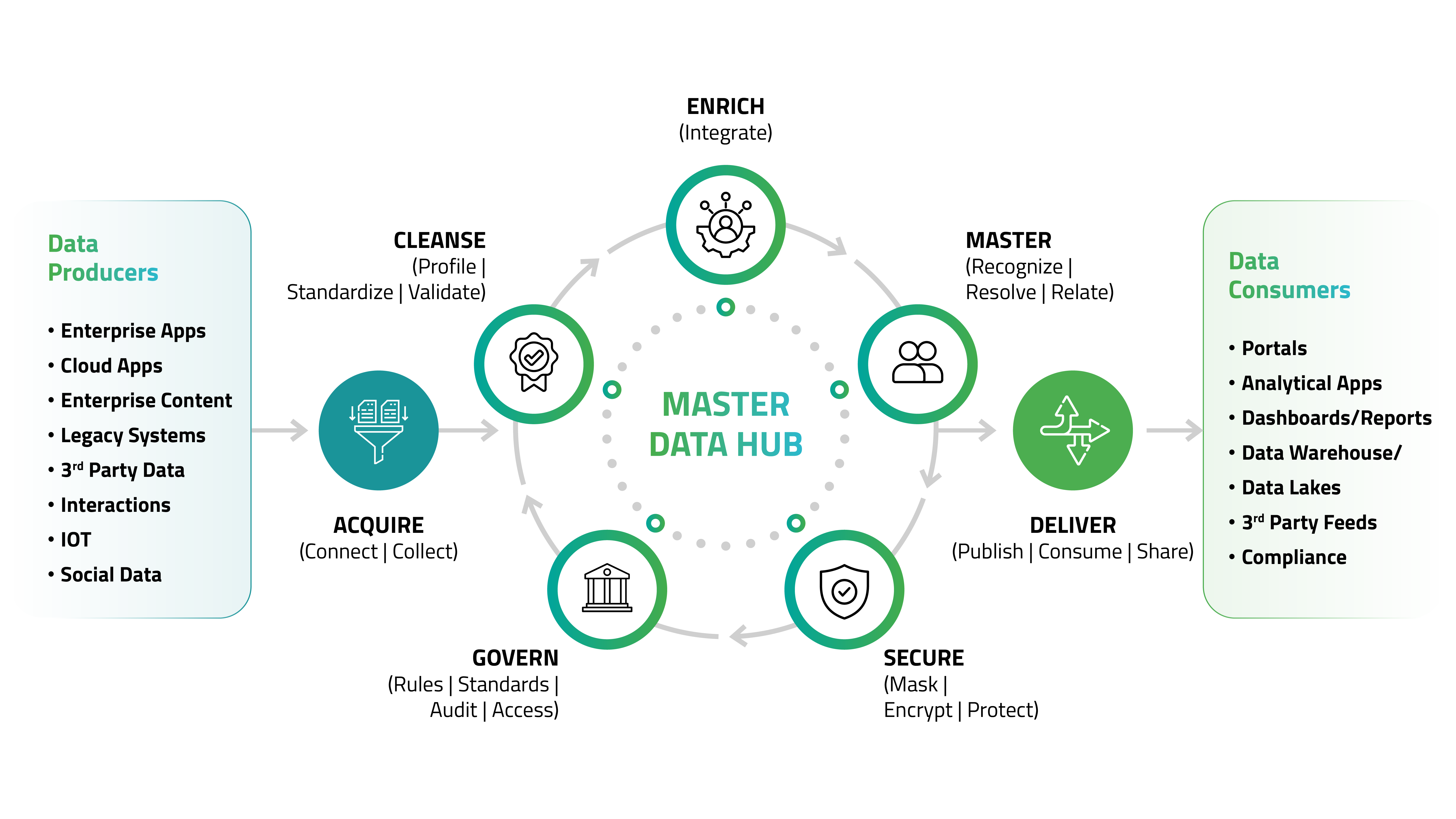
V. Understanding Master Data Management Architecture?
MDM Architecture refers to how a business’s data is recorded, documented and flows within the organizational structure. It shows how multiple data sources are connected and how data is organized to fulfil business objectives. The main aim of a master data management architecture is to construct a true picture of the flow of data to optimize the resilience, scalability, and performance of every system and process that supports master data across the organization.
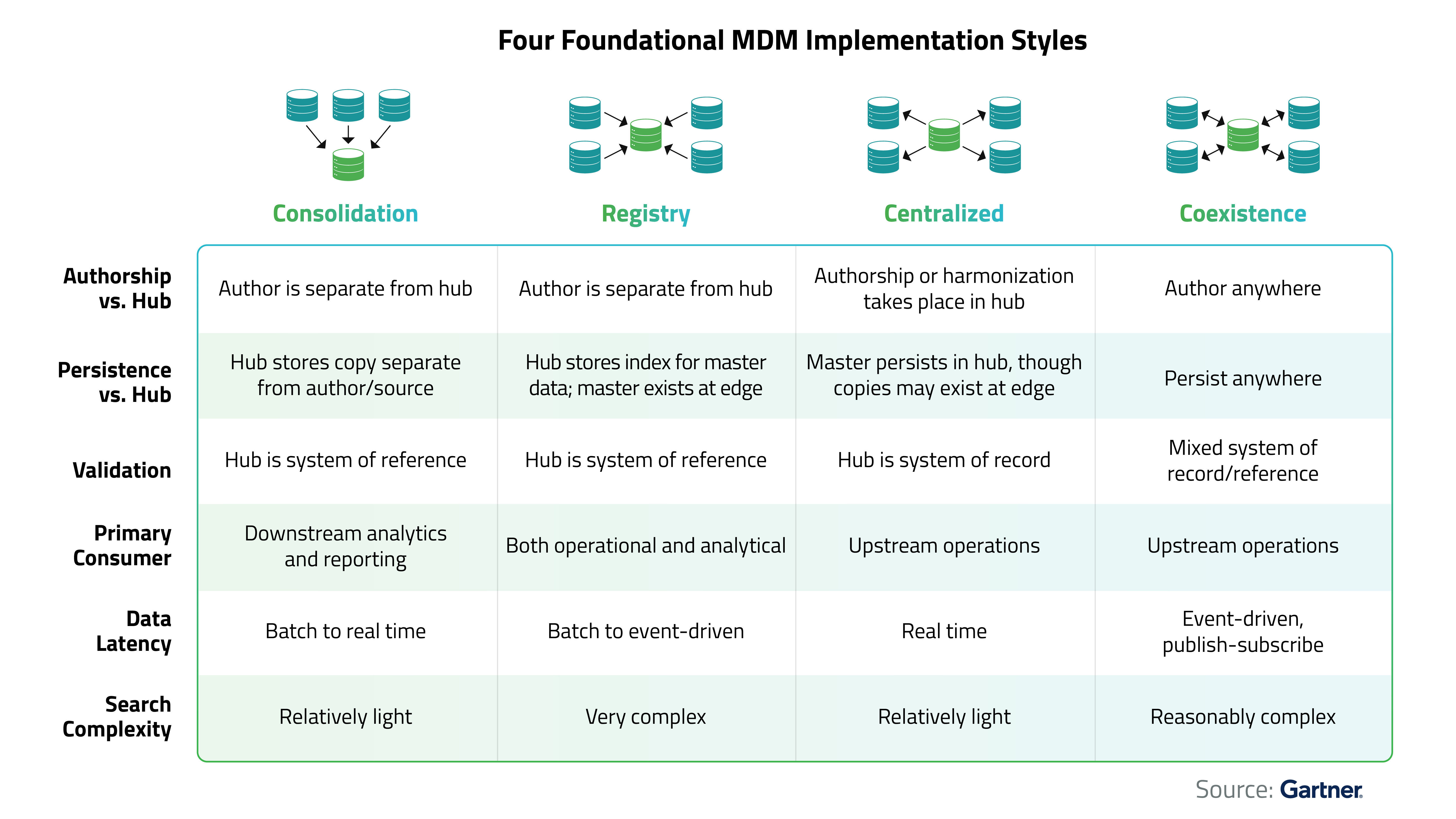
According to Gartner, there are four key MDM strategies, also called “implementation approaches,” (as they extend beyond architecture) which includes ‘technical setup’, ‘system structure’, ‘project scope’, and ‘impact on business processes and IT systems’. It is essential for businesses to know these approaches, match it with their organizational maturity and objectives and zero in on the right path. The chart here highlights the defining traits of each approach.
However, MDM styles are not rigidly distinct and can be combined or evolve over time. For instance, customer data may follow a consolidation approach, while product data may adopt a centralized model. Organizations often begin with a less disruptive style and gradually transition to more integrated models as they mature, like:
- Customer data may evolve from consolidation to coexistence as the organization develops.
- A consolidation-based analytical setup may shift toward a real-time, operational MDM environment under a centralized model.
- A hybrid approach is also possible, such as embedding a registry within a data warehouse to blend consolidation and registry styles.
Organizations typically choose the least intrusive style initially, ensuring early benefits while refining their approach over time.
VI. What is Master Data Governance?
As MDM involves not just management of critical master data assets but also change management, many MDM initiatives fail due to being driven solely by the IT. Due to lack of any engagement from business leaders, getting the authority to implement process and procedural changes becomes difficult. That is why an effective master data governance strategy is core to building a robust MDM strategy.
A strong data governance program ensures that top business stakeholders collaborate with IT and assign dedicated business roles—at executive, strategic, tactical and operational levels—to establish and enforce governance policies. It also includes mechanisms for resolving disputes and escalating issues, addressing key decisions such as defining a customer, determining data ownership, handling data, and classifying Personally Identifiable Information (PII).
Successful Data Governance programs share key characteristics, including:
- Enterprise catalog that devises clear and consistent policies to comply with organizational standards and regulations
- Security and data privacy policies
- Data access and right management
- Dispute resolution protocols
- Continuous data quality monitoring
VII. MDM and GenAI
GenAI with MDM Integration has ushered in a new era. It has revolutionized data quality and management, empowering organizations to utilize their master data like never before. This fusion is all set to accelerate informed decision-making, make strategic improvements, equipping businesses for high-end agility, data-driven future via predictive insights. Some of the ways in which Gen AI is transforming MDM is through:
- Advanced Categorization: By automating text classification, product categorization, and hierarchical mapping Generative AI improves search, navigation, and data relevance while reducing errors. Altogether, it streamlines data categorization, easing the management of vast master data volumes.
- Data Discovery: Through uncovering hidden elements of information, Generative AI classifies data fields and assigns them semantic labels to expedite creation of master data definition. It also assists in identifying new master data domains through entity discovery.
- Data Acquisition: By automating attribute identification and data ingestion, Gen AI aligns fields with existing master data models. It accelerates bulk uploads, recognizes entity types, and supports content creation, translation, and image recognition.
- Data Match-and-Merge: By automating data matching rules and deduplication, Gen AI enhances precision, consolidates low-scoring data matches, and creates hybrid golden records, ensuring data consistency and reliability.
- Data Modeling: Generative AI automates schema matching and model cataloging, reducing human errors and improving alignment across varied and dynamic data schemas such as Microsoft Dynamics 365, Salesforce, or SAP. It recommends core attributes and optimizes data structure for unique business needs.
- Data Quality: Gen AI automates rule recommendations, generates dashboards, and enables smart fields (for common data fields e.g., addresses, phone numbers, and emails), while standardizing data validation to enhance accuracy and consistency.
- User Experience: Considerable ease of use is witnessed through the deployment of AI assistants, conversational interfaces, and personalized dashboards to access data, simplify analysis, reduce training time, and enhance user adoption.
- Governance: Gen AI automates data associations by linking business definitions, policies, and data ownership, considerably improving cross-functional collaboration. It also automates stewardship tasks and interpret and leverage unstructured data.
- Compliance: By automating data classification and PII detection, Generative AI speeds-up regulatory adherence to major industry standards and necessary compliances, hence bolstering security protocols.
- Data Sharing: Gen AI enhances secure data exchange, enabling intelligent automation, governance-compliant frameworks, and advanced content-based filtering to deliver precise, actionable data, while minimizing human error.
Also read: The Relevance of PIM in Driving Digital Transformation
VIII. Why MDM is Turning Essential Today?
MDM is considered today as the cornerstone of digital transformation and business adaptability. Industry leaders have already established a direct correlation between master data entities and key business objectives such as customer loyalty, supply chain efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Here are some of the significant business impacts of master data management system:
- Strengthened Integrity of Business Data: Fragmented and inconsistent master data across complex IT ecosystems reduces trust in both data quality and decision-making. Companies are increasingly acknowledging the direct impact of master data management on their strategic goals.
- Application Modernization: Digital transformation is compelling organizations to initiate or upgrade their MDM programs. Most MDM platforms are now leveraging modern cloud solutions and advanced capabilities.
- Business Agility and Resilience: Evolving market demands, particularly in uncertain times, amplify the need for reliable, connected data and robust processes, that MDM provides.
- AI and Analytics: Large-scale AI adoption has intensified the necessity to create a structured, trustworthy master data foundation in order to draw valuable AI-driven insights.
- Cloud Adoption: The rise of cloud-based and subscription-pricing models has made MDM more accessible beyond large enterprises. Nearly all new MDM implementations now leverage cloud technology.
- Multidomain Expansion: While customer and product MDM remain prevalent, organizations are broadening their focus to encompass additional domains—such as location, asset, employee, and supplier MDM—to comprehensively address operational and compliance challenges.
- Simplified Deployment: Concerns over MDM’s complexity and cost have diminished with cloud-based solutions, user-friendly interfaces, and a shift toward modular, outcome-driven implementations. Many master data management vendors are also coming up with phased deployment strategies.
Also read: Discover New Growth Paths with AI-Driven Data Management
IX. Which Industries use MDM?
- Retail: MDM expedites data onboarding, boosts agility, streamlines processes for customer-centric personalized offerings, and empowers retailers with a unified view of data. By capturing insights from multiple sources and channels, the MDM platform unveils buying patterns to aid real-time decision-making. And through pre-configured dashboards, data models, and business rules, master data management speeds up innovation and digital transformation.
- Manufacturing: By integrating data from multiple systems, MDM streamlines compliance, automates workflows, and synchronizes information for manufacturers. It also standardizes data for suppliers, distributors, and end-users. And with seamless bi-directional data sharing, real-time analytics and AI-driven insights, MDM mitigates risks, supporting strategic decision-making, accelerating product launches, while significantly boosting efficiency and growth.
Also read: Product Information Management (PIM) for Manufacturing
- • CPG: CPG companies need to tailor their data as per enterprise specific guidelines, nomenclature, and product classifications. MDM standardizes diverse retailer inputs, ensuring uniformity in data such as, zip codes, product names, and other information, eliminating inconsistencies and duplicates. By providing a consolidated, accurate data source, MDM optimizes reporting and supports agile response to market shifts.
- • Automotive: MDM standardizes diverse data formats, such as details of make, model, and year for OEM (Original equipment manufacturers) and aftermarket parts and keeps costly errors at bay for the automotive industry. MDM streamlines operations by centralizing data to aid manufacturers and suppliers, thereby enhancing efficiency, and compliance in the dynamic automotive industry.
X. Master Data Management Best Practices
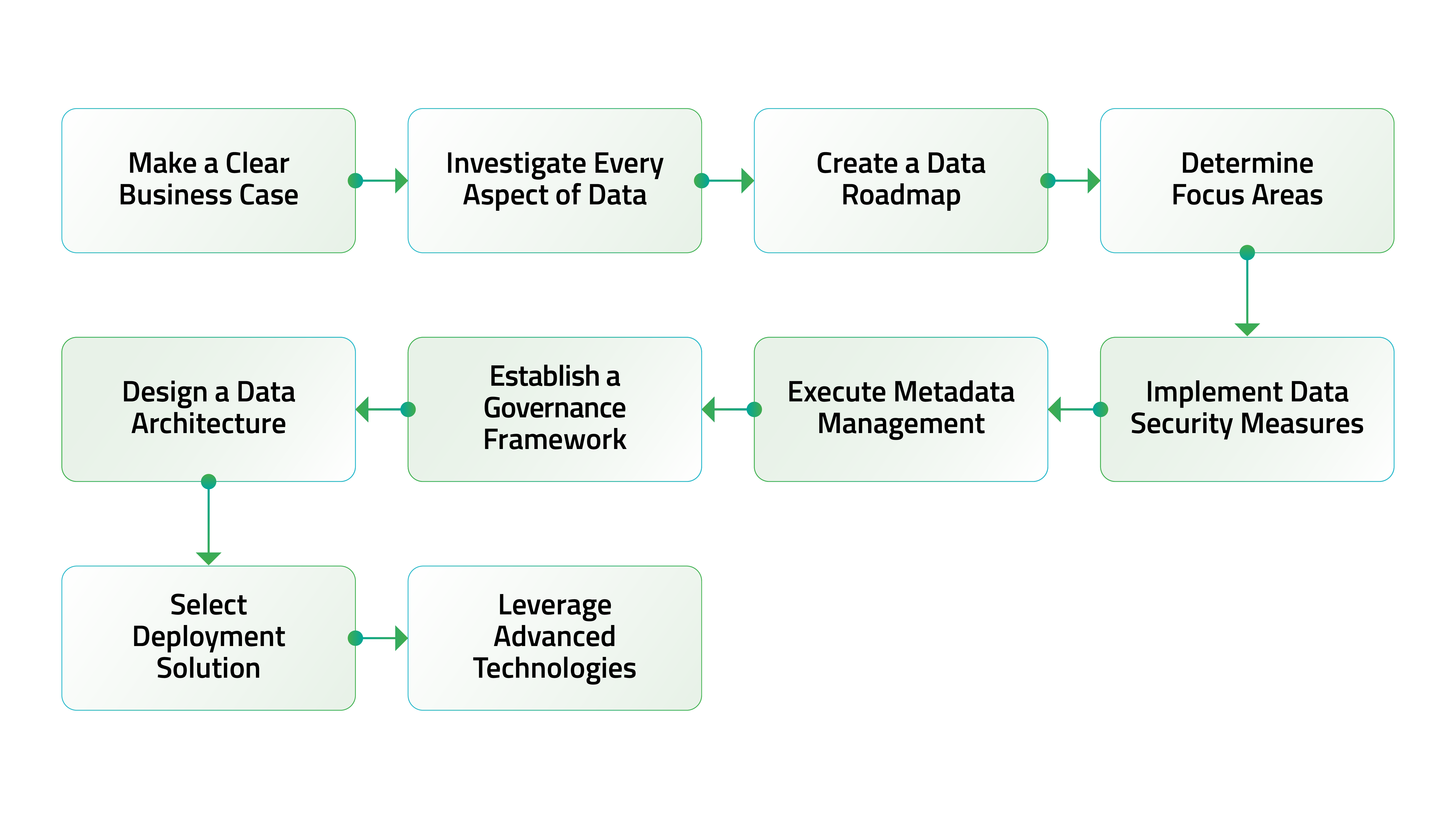
Building an efficient data management system requires a structured strategy and a clear grasp of your organization’s needs and objectives. Some of the essential steps are:
- Make a strong business case
- Define core objectives, vision, and strategy for MDM
- Get Buy-in from top stakeholders
- Carry out thorough investigation
- Identify problem areas
- Estimate the impact of poor data
- Determine data sources and key data elements
- Create a strategic data roadmap
- Work out a collaborative approach between IT and various departments
- Evaluate data quality
- Implement processes for data accuracy, completeness, and consistency
- Determine top focus areas
- Identify critical data domains
- Prioritize quick wins
- Design a data architecture focusing on
- Integration with data sources
- Scalability
- Real-time integration
- Best possible data synchronization
- Establish a governance framework
- Outline policies and guidelines
- Specify protocols and standards
- Define data access and right management
- Implement metadata management for better data discovery and comprehension
- Enforce strong security measures
- Safeguard data from breaches
- Prepare for emerging cyber threats
- Test security measures continually
- Select appropriate deployment solution
- On-premises
- Cloud-based
- Hybrid
- Leverage advanced technologies
- GenAI
- Machine Learning
- Advanced Analytics
XI. How to Choose the Right MDM Platform
With every enterprise requirement being unique, it is imperative to understand the strengths of any MDM platform you are considering. Key aspects such as syncing with your digital infrastructure, alignment with business objectives, and cost can make a huge difference. Some of the key considerations are:
- Meeting (unique) Business Needs: The MDM system must fit the scope, scale, and complexity of your business case. It should be able to provide the right solution for our chosen data domains (customer, product, etc.) and must fulfil your unique needs.
- Flexibility and Adaptability:
- A flexible data model is key to adapting with enterprises’ current and future needs. Data models would likely require regular modifications to meet evolving business demands. Hence, a master data management platform that offers the right flexibility to customize must be prioritized.
- Integration: It’s crucial to assess the MDM solution’s ability to seamlessly connect with databases, applications, and various platforms. Integration must ease data ingestion, transformation, and synchronization, and offer support for real-time integration, data streaming or batch processing.
- Data Quality: The platform must ensure high-end data quality management including accuracy, enrichment, completeness, and validation. Look for features that enforce data quality rules, especially de-duplication, to focus on master data uniqueness and consistency.
- Data Governance: The platform must accompany a robust data governance framework that defines clear-cut data governance policies, rights, and access management to establish clear accountability, so support data integrity, security and compliance.
- Ease of Use and Training: Assess the platform’s user interface, navigation, and overall user experience. Also, determine the ease of user training, available learning resources or documentation, and the level of support available for team members.
- Scalability: Evaluate competencies to handle large data volumes, complicated data processing, and concurrent usage. Also, assess the abilities to scale horizontally or vertically, and features such as data partitioning, indexing, caching, etc.
- Security & Compliance: Assess core security features such as data encryption and authentication, data access controls, and data masking to ensure the security requirements are met properly. Besides, the platform must adhere to major industry regulations and compliances such as ACES/PIES, HIPAA etc.
- Future-Readiness & Stakeholder Involvement: Choose a solution adaptable to AI, IoT, and cloud advancements. Engage top stakeholders from technical and business teams for assessing the current stage of their platform’s progress in future technologies and the roadmap ahead. This is crucial to enterprise growth plans.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Calculate the total cost, including licensing, implementation, customization, and maintenance, as well as hardware and infrastructure requirements. Also, determine whether it aligns with your enterprise budget and offers a strong return on investment (ROI).
Get Your Industry-Specific MDM Solution with Happiest Minds!
We implement industry-tailored MDM solutions and specialize in aligning your data with your business vision.




